Google Shopping is one of the most widely used product feed formats in Mergado. In partnership with Proficio, a Google Certified Partner, we’ve described the seven most common issues you may encounter at the Google Merchant Diagnostic Center. We are also going to show you ways how to fix them in Mergado.
1. Category mapping
Google Shopping has its specific category tree, which is the alpha and omega of the successful product listing. So mapping the correct categories will probably be the first change you need to make. Mergado knows Google categories. So you can map them correctly with a few clicks.
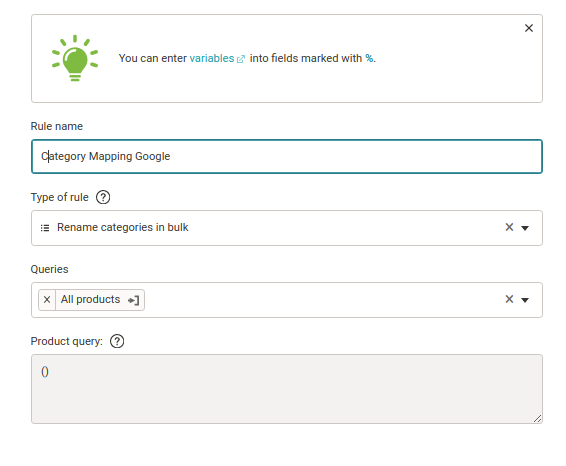
1. In Mergado in Google Merchants Export, go to the Rules section and click New Rule (or use the keyboard shortcut Alt + T).
2. Name the rule — for example, Category as Mapping Google, and then select the Rename Categories in Bulk rule that is specified for this type of editing. Apply it to all products.
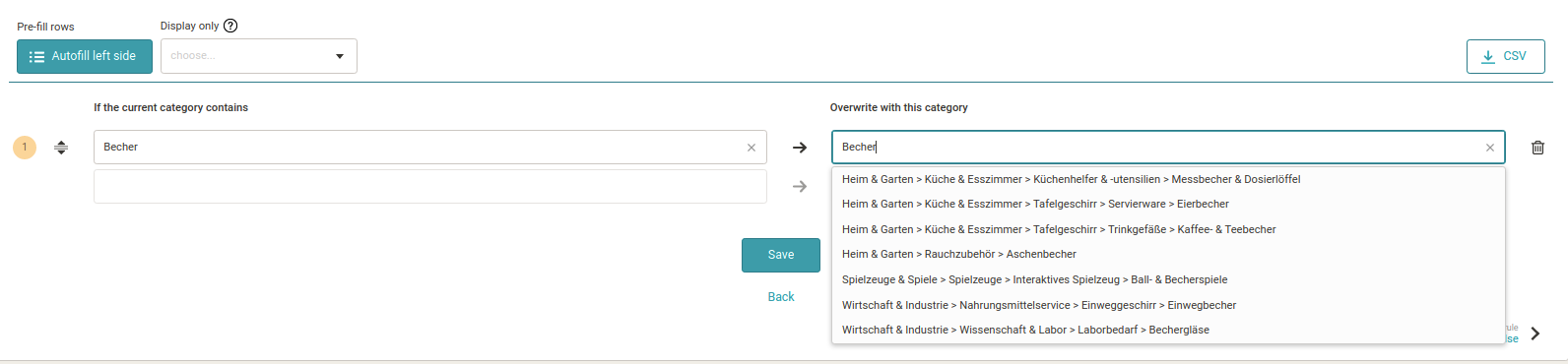
3. The Autofill left row button automatically lists all the categories that your feed contains in the left column. Then use the insinuator in the column on the right to select the appropriate Google category. Finally, click Create to save the rule.
4. You can return to the created rule at any time and edit it on the Rules page.
2. Missing identifiers
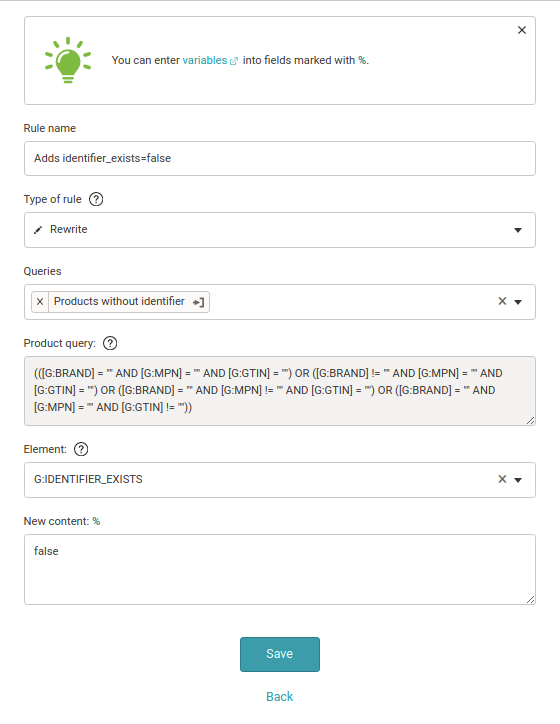
The BRAND, GTIN, and MPN identifiers are used in the Google Merchant feed for correct product identification. Google requires at least two of these three identifiers for each product. If your products have only one or no identifier, you need to add the element g:identifier_exists to each product and fill it with the value false (alternatively, the no value also works).
In Mergado, you can use the Rewrite rule for this type of feed edit.
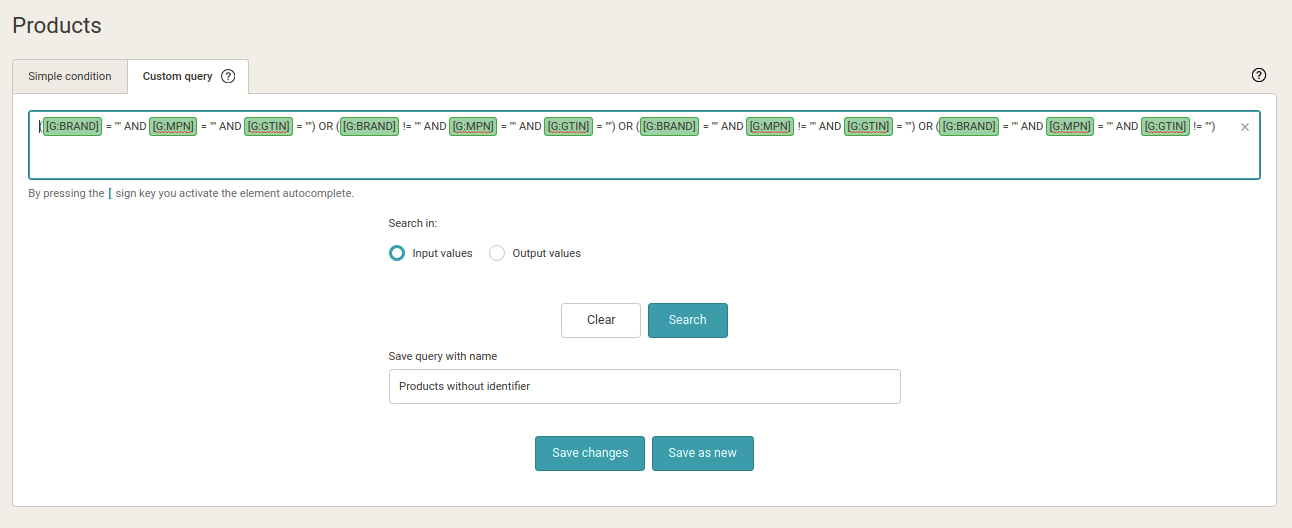
1. First, in the Products tab, define a product query that contains products with only one or no identifier. In the Custom Query tab, you define a set of such products with the following expression: ([G:BRAND] = “” AND [G:MPN] = “” AND [G:GTIN] = “”) OR ([G:BRAND]! = “” AND [G:MPN] = “” AND [G:GTIN] = “”) OR ([G:BRAND] = “” AND [G:MPN]! = “” AND [G:GTIN] = “”) OR ([G:BRAND] = “” AND [G:MPN] = “” AND [G:GTIN]! = “”)
2. Name and save the product query. For example, under the name Products without an identifier. This query updates itself automatically, and Mergado keeps it up to date.
3. Now go to the Rules tab and create a New Rule. You can call it Adds identifier_exists = false. Select the Rewrite rule type and apply Products without an identifier to the product query. Choose the element you want to fill — in our case g:identifier_exists and fill it with the false value.
4. Now, all you have to do is save the rule by clicking Create.
5. You have just filled in the missing identifiers.
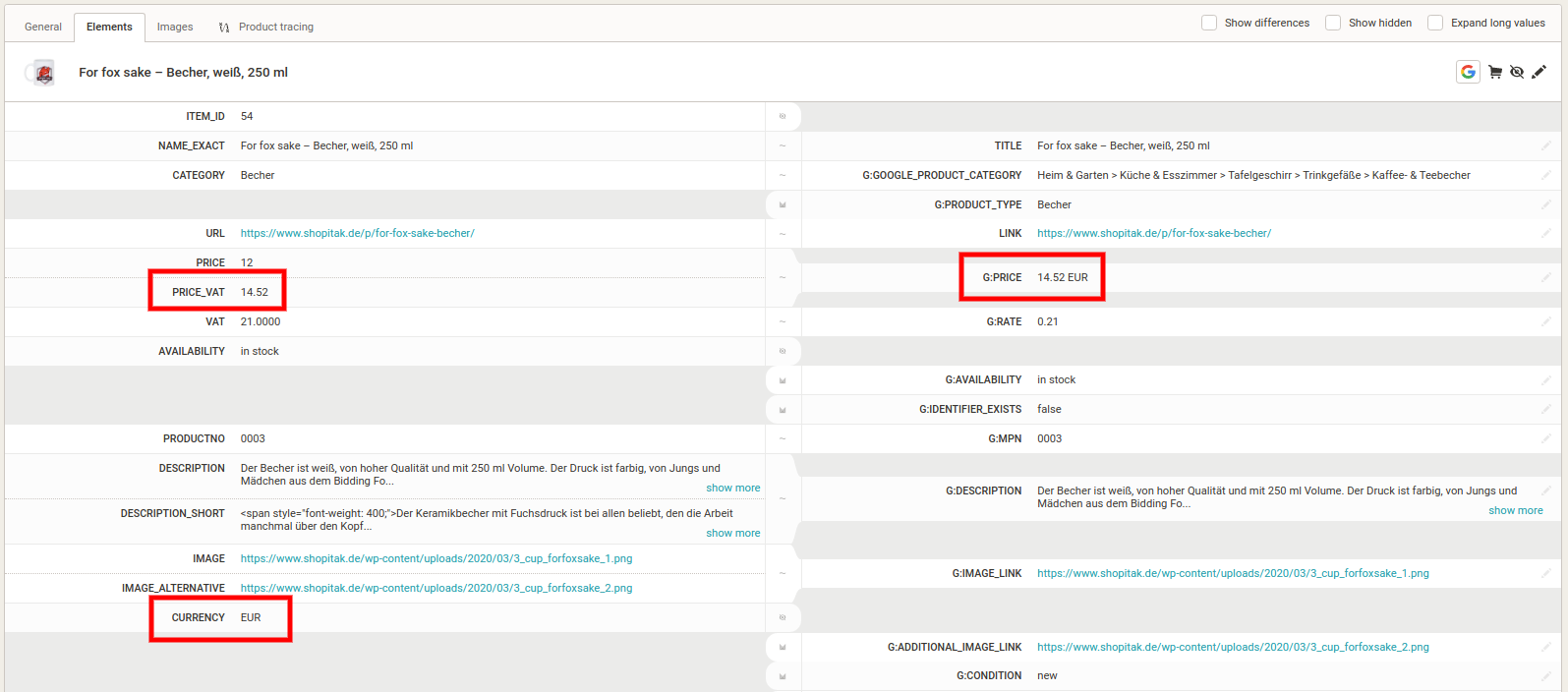
3. Adding a currency to the product price
In the g:price element, Google requires both a numeric value and a currency. If you have the price of goods and currency in two different elements in the input feed, Mergado automatically combines these two variables into the g:price element when converting the feed to Google Merchants format. No further adjustments are required.
If you later need to remove or change the currency for some reason, you can do so using the Find and Replace rule. You replace the character string corresponding to the currency abbreviation with an empty value or an abbreviation for another currency in the g:price element.
4. Minor image corrections
A common problem is the relative URL of the image in the IMG_URL element. Of course, such an image will not load in Google Shopping. If you have product images stored on a local server and use only a relative URL, you need to edit it in Mergado. The solution is the Find and Replace rule. At the beginning of the relative URL, you add the domain URL of your online store.
We recommend the Feed Image Editor app for advanced image editing, including image auditing.
5. Minor price problems
Submitting prices to Google can sometimes be a hassle, especially if you have more than one price on the web. In Mergado, you can easily define which value from your original feed you want to send to the g:price attribute.
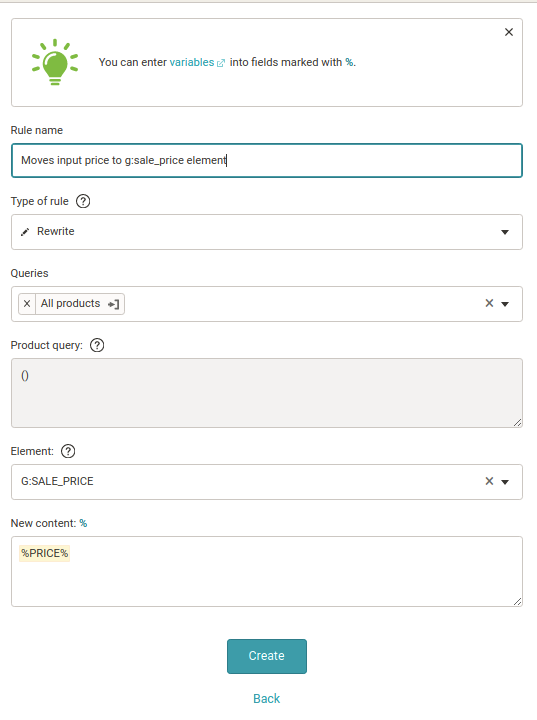
As a practice example, imagine a situation where, for some reason, the sales and discount price attributes are being sent incorrectly. The discount price is exported to the g:price attribute, the sale price to the g:sale_price attribute. But it should be the opposite. In Mergado, you can use the Rewrite rule to “flip” values to the correct attributes. You need a total of two rules for this.
1. Create a Rewrite rule. For example, call it The rule converts the sale price to a discount price.
2. Apply it to all products.
3. The element you want to overwrite is the g:sale_price element.
4. As new content, which you want to fill the g:sale_price element with, select the price attribute variable from the original feed. That is the sale price, which is exported incorrectly from the store.
5. Using the opposite logic, create the second rule called The rule that converts the discount price to the selling price. In this case, you populate the g: price element with an attribute variable for the discount price from the original feed.
6. Custom label
Google allows you to create up to 5 custom labels for each product to manage your campaigns more effectively. In practice, this means that you can add information to products in the Google feed that the customer will not see anywhere. But you may internally box the products according to specific attributes. Typically, this can be PNO, seasonality, margins, or best-selling products. You’ll then set your campaigns with these labels in mind, not only for Google Shopping but also for Google Ads.
1. Create a new element in Mergado named g:custom_label_0.
2. Use the Rewrite rule to fill it with the required values. You can fill the label with the values of the corresponding element from the original feed or create product queries based on the rules, which you can then manually fill with specific values in the Rewrite rule. Alternatively, you can use the Data File Import rule, which you use to pair values from an external CSV file to specific products.
7. Smart campaigns
Google allows you to set up so-called smart campaigns. They are based on machine learning, and they simplify and streamline advertising. The key is to have a feed available at all times. When Google notices an advertiser outage, smart campaigns are paused, and it can take up to 14 days for ads to be “re-learned” and resumed. Even in this case, Mergado is a good assistant. Because in the event of a failure on the online store side, it always sends the latest updated version of the feed to Google.
If you choose to advertise on Google Shopping, you probably encounter these issues. Fix them according to our instructions in Mergado and tune your Google feed to perfection. Can you think of any other common Google feed problems? Let us know in the comments what you optimize most often.


The co-author of the article is Adam Funiok of the Proficio agency.
Read more: